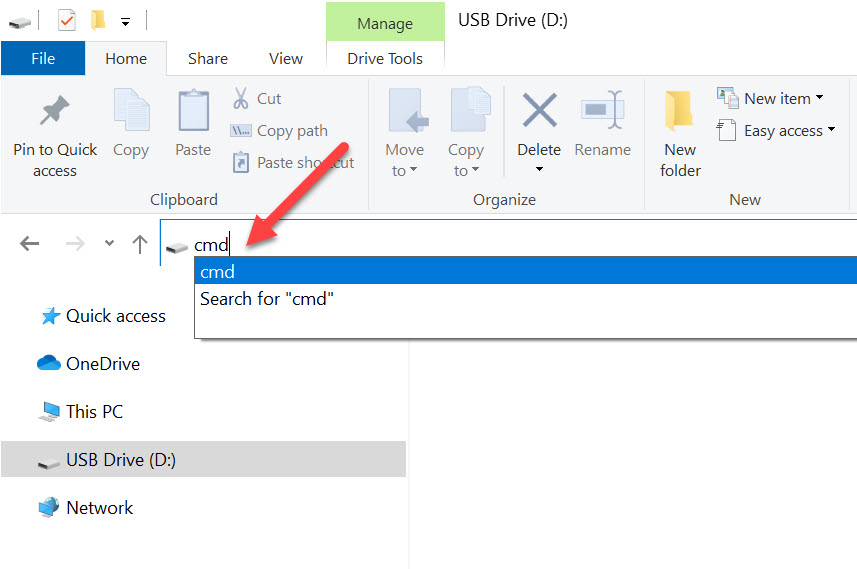
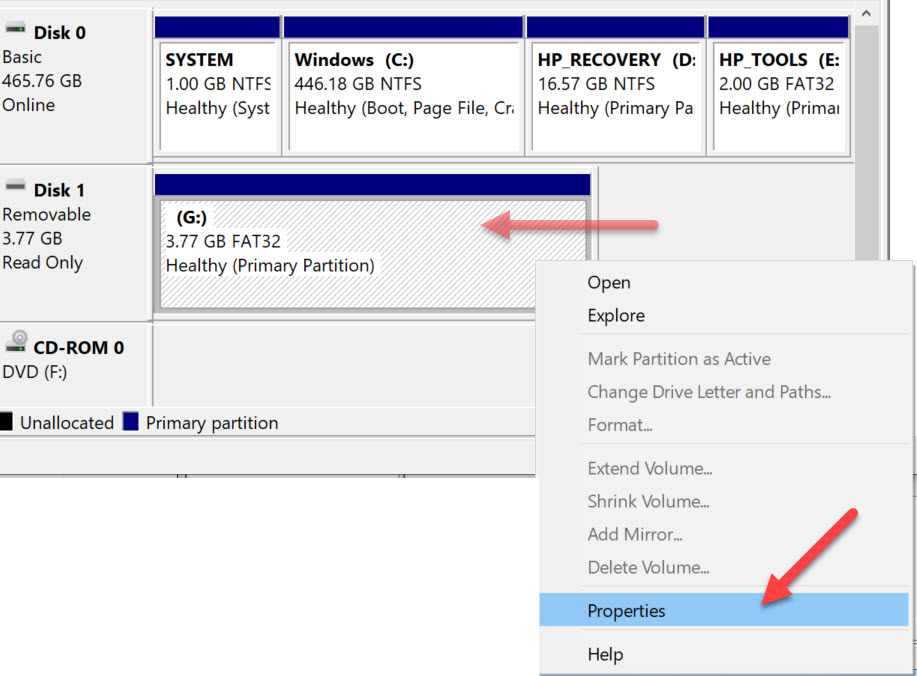
Solved: Can’t Mount IMG File in Windows 10
The first thing to understand is that image files are a messy business. There is plenty of cross-over information and functionality between image file extension types – it is easy to get confused!
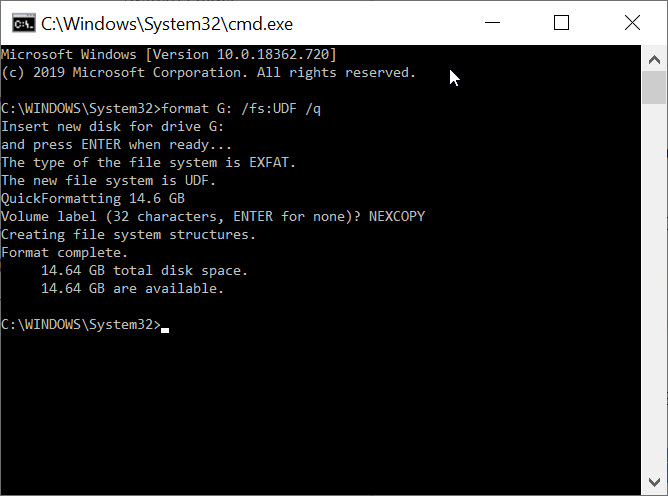
Don’t be surprised if you can’t mount an .img file in Windows 10 with their default utility – it’s a common problem and this article will help.


It is important to understand not all image files are the same. Heck, not all .img files are the same. Some basics: For the term “image files” you typically see .img files and .iso file extensions and they have similar functionality and conceptually accomplish the same goal. The goal is for an image file to hold digital content, in a single file, of a file system and a its set of data. If that sentence is confusing, then maybe think of an image file this way: a zip file (but without compression).
A very quick summary explaining the difference of .img and .iso image files. An optical disc holding data is configured differently than hard drive storage space. The optical disc has data written in a linear configuration and is a digital binary copy of the ISO 9660 standard or derivative UDF standard. The ISO file extension is a single file which contains all the digital information just described.
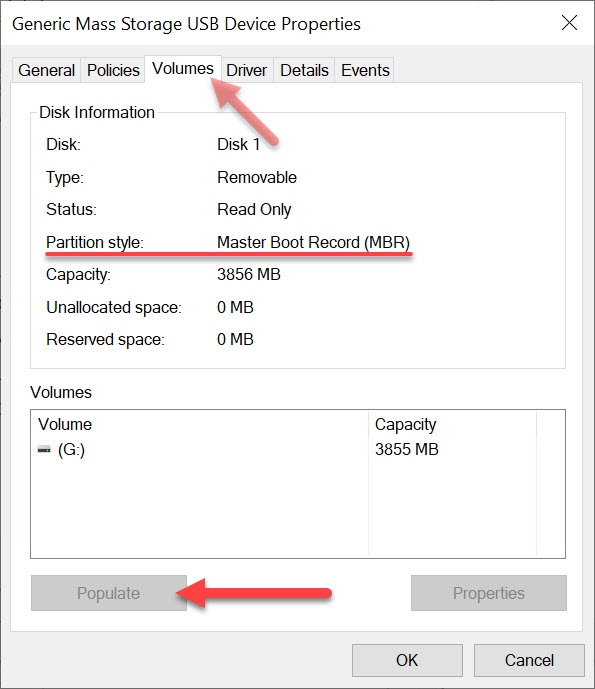
An .img file is a digital copy of the contents of a hard drive or flash drive. Technically you can have an .img of a CD or DVD as well, but most should associate the image of a disc as ISO. An .img file is a disk image which begins with a FAT sector which is used to identify the file system and files contained inside the image file. The image file of a disc (ISO) begins with a descriptor file which describes the layout of the disc.
That last sentence is important: