CD and DVD optical duplicators have been popular for years; however, with the disc drive no longer sold in computers, the only device left for moving files around are USB flash drives – well, most common device at least. With that in mind, let us provide a USB duplicator review and our observations about them.
So what is the speed of burning a DVD compared to copying to a USB flash drive? With a 16X DVD recorder it will take about 6-7 minutes to burn an entire disc, which is 4.7GBs. A common size DVD duplicator is seven drive system which means 7 copies every 7 minutes. However, today’s file sizes are getting larger and a data load can easily be over 5GBs. A dual layer DVD is 8.5GBs and would take about 27 minutes.
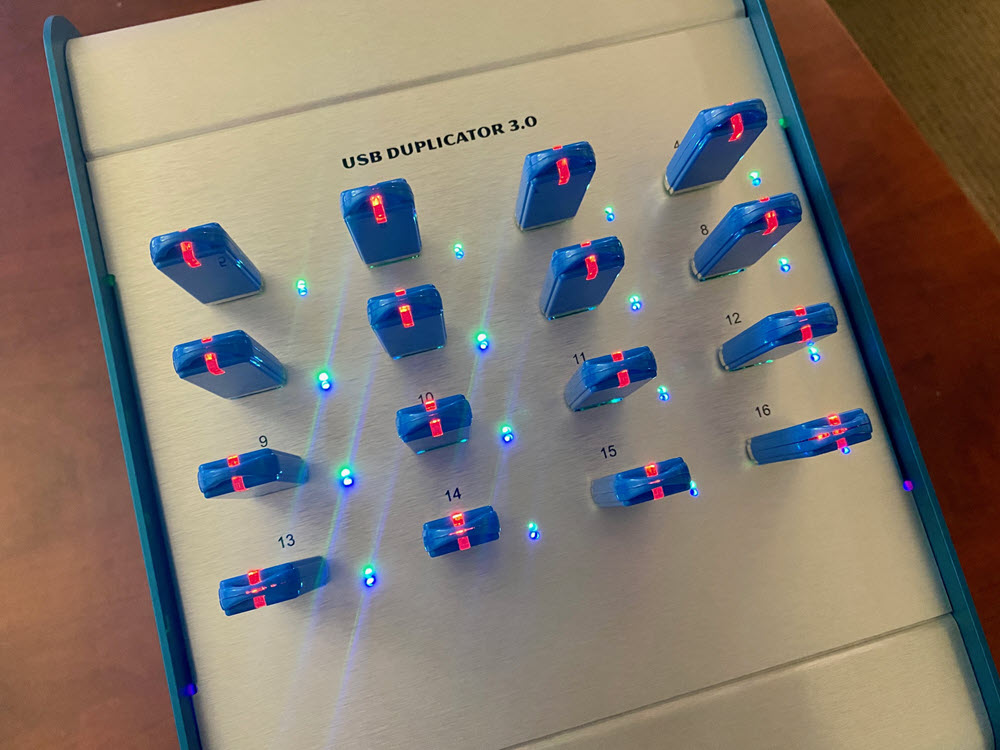
The USB duplicator in this review is a sixtenn target USB 3.0 duplicator manufactured by Nexcopy. This model was selected because it was the most popular in search results, and honestly – looks best for an office setting. This system will make sixteen copies at 1GB under a minute; which translates to 16 copies in less than five minutes. The dual-layer DVD mentioned above would be 9 minutes to make 16 copies. Clearly a USB duplicator is more efficient than a DVD duplicator.
OVERVIEW
Nexcopy’s model in today’s review is the USB160PC. This is a Windows computer based software and hardware solution which runs on Windows 7 or Windows 10. The copy speeds are the same as designated standalone systems. Below is a picture of the PC based system and the standalone system, both about the same port numbering (16).

The USB160PC uses software and provides six copy modes which a company can chose which copy method is best for their needs. Copy modes are:
- File Copy
- Copy Add
- Device Copy – Data Only
- Device Copy – Full Media
- IMG Copy
- Unique Data Streaming
We will cover the copy modes a bit later in the review.
The Drive Manager software by Nexcopy, has a data extraction feature giving the user the ability to extract data off the drive and make a data dump to a location on the host PC.
The PC based USB duplicator is fast and flexible to work with and provides excellent user feedback during the duplication process. The GUI (Graphical User Interface) ties in the obvious information such as USB flash drive total size, bytes used, percentage done during duplication and pass/fail response. Nexcopy uses their own Drive Manager software (trademarked) and provides lifetime software support and updates for free.
The GUI does an excellent job of identifying the USB device shown in the software with the USB socket on the duplicator. This is one problem with any home-grown duplication system, like connecting flash drives to a USB hub – the only way to identify a drive is by disconnecting it until you’ve found the one in question. The USB160PC gives you the tools to quickly identify each USB drive connected.

The bonus information from Drive Manager is the second tab of the GUI. This page shows the device serial number, the VID (Vendor ID) the PID (Product ID) and device descriptor information. The tech folks will appreciate this feature.
HARDWARE
For this USB duplicator review we weighed the duplicator box and it came in just under 5 pounds – so portable! Two LED for feedback along with the GUI software. Blue LED shows power to the socket and green LED displays activity of the device (will blink when reading or writing data). The GUI will provide performance feedback and status about the copy job and process. The power supply is auto-detecting and will automatically work in a 110v or 230v environment, no need to make a manual power setting switch with the physical box. The USB duplicator has a 5v fan on the back side to provide air flow for cooling; although we didn’t experience any heat during testing and operation.
The power supply inside is a 150watt MeanWell brand power block, which is a brand used by medical companies so power will never be an issue. This also means the 150watt power supply can support 16 USB hard drives.